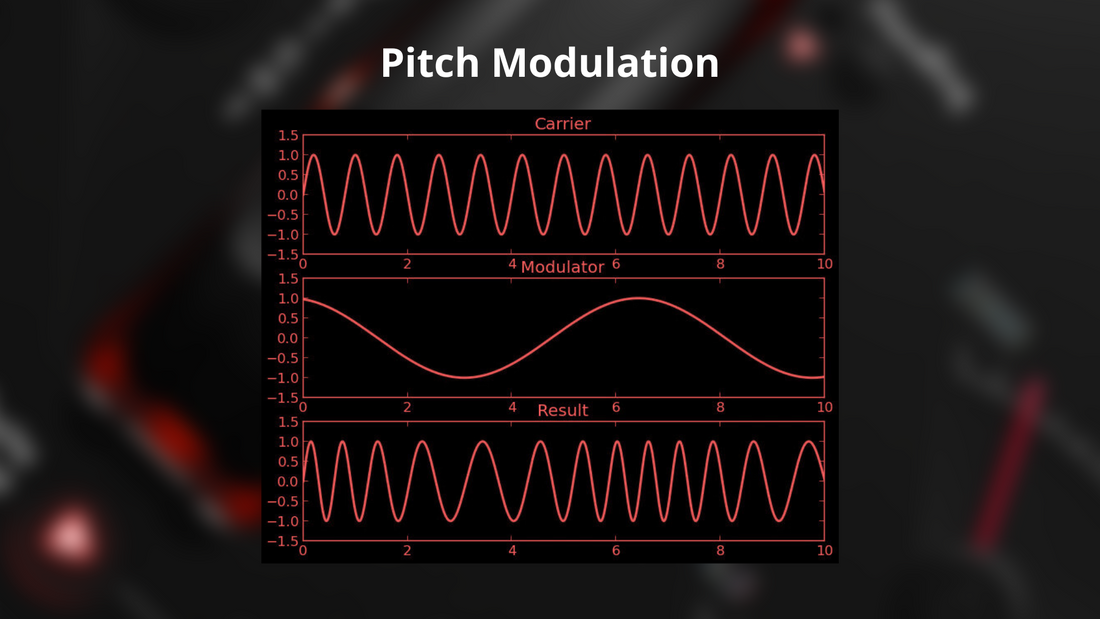
Pitch Modulation in Digital Signal Processing (DSP)
Pitch modulation in digital signal processing (DSP) refers to the process of altering the pitch of an audio signal without affecting its speed. This is commonly used in synthesizers to create dynamic, expressive sounds. However, pitch modulation can also be applied to other audio signals using a real-time time-stretching algorithm, which enables pitch adjustment while preserving the original duration of the audio. This technique is used in applications like voice processing, music production, and even sound design, where pitch changes are required without distorting the timing or tempo of the signal.
Real-time Pitch Modulation with APM Live

Pitch Modulation is commonly known for its use in a synthesizer using a Modwheel. Typically, a LFO (Low Frequency Oscillator) modulates the pitch of the other oscillator(s) used for creating the sound when Moving the Modwheel. This technique 'was' limited to synthesizers until APM Live came around. It uses a Realtime Time Stretching Algorithm to Modulate Pitch in Realtime. Allowing the use in a wide range of applications, such as live guitar pitch modulation , live vocal modulation, Live Instrument modulation, realtime vocal effect, realtime guitar vibrato, realtime vibrato effect etc.
Techniques:
Several techniques are commonly employed in DSP for pitch modulation:
-
Frequency Shifting: Frequency shifting involves adding or subtracting a fixed amount of frequency to the entire spectrum of an audio signal, effectively changing its pitch while preserving its harmonic structure.
-
Phase Vocoder: The phase vocoder is a time-domain analysis-synthesis technique used for time-stretching and pitch-shifting of audio signals. By decomposing the signal into its constituent frequency components, the phase vocoder allows for independent manipulation of pitch and time.
-
Granular Synthesis: Granular synthesis involves breaking down audio signals into small, discrete grains and manipulating their pitch, duration, and spatial properties independently. This technique enables the creation of complex textures and evolving soundscapes.
-
Pitch Correction: Pitch correction algorithms detect and adjust the pitch of individual notes in vocal or instrumental performances to correct inaccuracies and achieve desired tuning standards. These algorithms analyze the spectral content of the audio signal and apply corrective pitch shifts in real-time or offline.
Applications:
Pitch modulation in DSP has a wide range of applications across various domains:
- Music Production: In music production, pitch modulation is used to create harmonies, melodies, and special effects, enhancing the creative possibilities of composers, producers, and sound designers. Check out APM Live
- Sound Design: In sound design for film, television, and video games, pitch modulation is employed to generate unique sound effects, atmospheric textures, and immersive sonic environments. Check out APM Live
- Live Performance: Pitch modulation techniques are used in live performances by musicians and electronic artists to manipulate the pitch of audio signals in real-time, creating dynamic and expressive musical experiences. Check out APM Live
- Voice Processing: In telecommunications and audio communication systems, pitch modulation is utilized for voice processing applications such as pitch shifting, gender transformation, and vocal effects generation. Check out APM Live
Conclusion:
Pitch modulation in digital signal processing is a versatile and powerful tool for audio manipulation and creative expression. By leveraging advanced algorithms and signal processing techniques, DSP enables precise control over pitch modulation while preserving the integrity and fidelity of the original audio content. From music production to sound design and live performance, pitch modulation continues to play a crucial role in shaping the sonic landscape of modern audio production and technology.